It started with a whimper a couple of years ago and has turned into a roar: foreign governments are dumping US Treasuries. The signs are coming from all sides. The data from the US Treasury Department points at it. The People’s Bank of China points at it in its data releases on its foreign exchange reserves. Japan too has started selling Treasuries, as have other governments and central banks.
Some, like China and Saudi Arabia, are unloading their foreign exchange reserves to counteract capital flight, prop up their own currencies, or defend a currency peg.
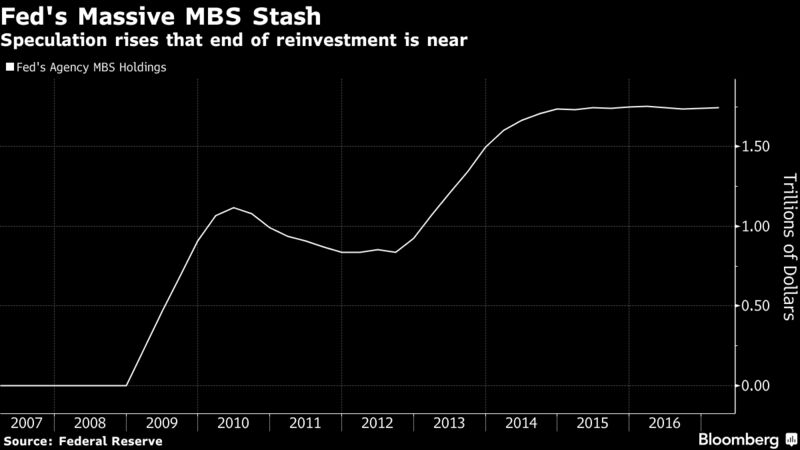
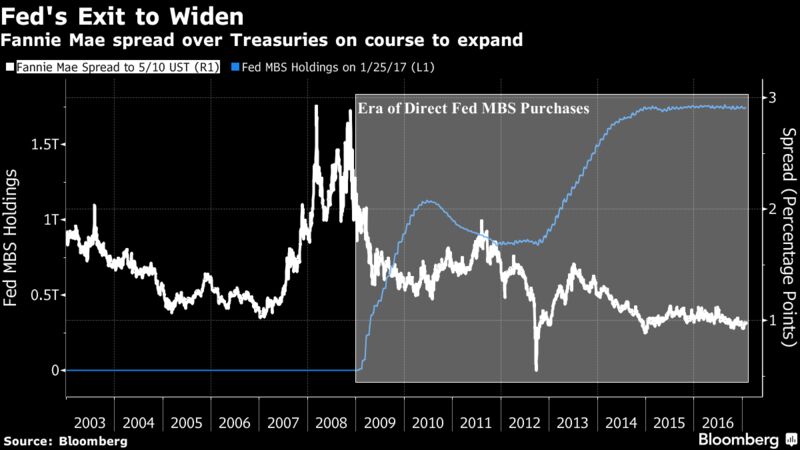
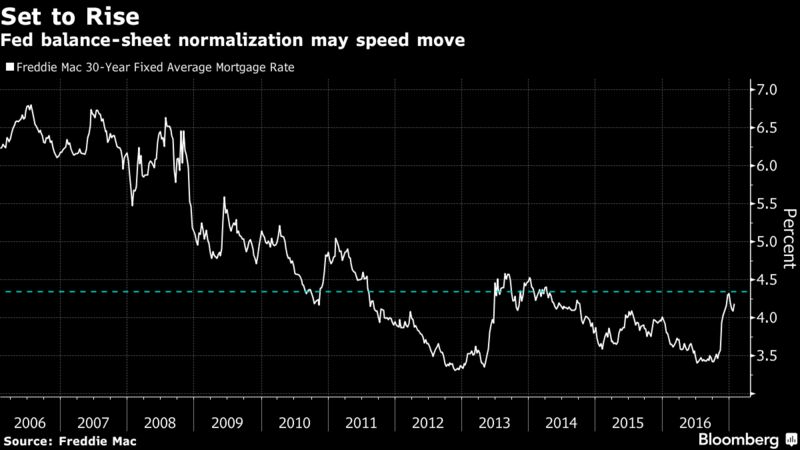
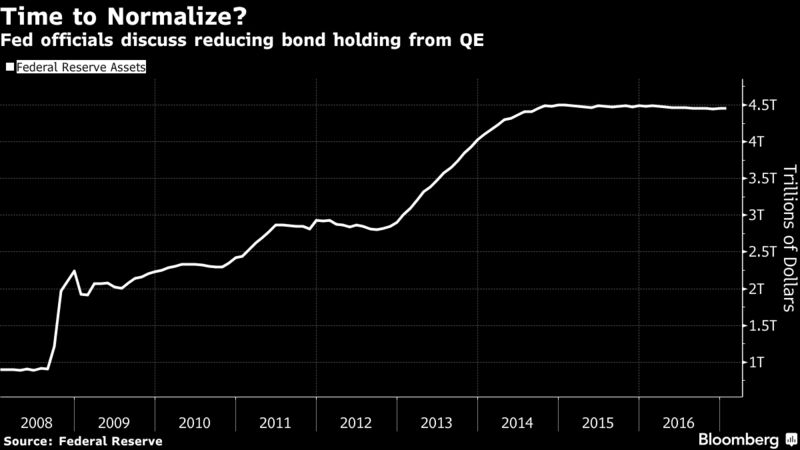
Others might sell US Treasuries because QE is over and yields are rising as the Fed has embarked on ending its eight years of zero-interest-rate policy with what looks like years of wild flip-flopping, while some of the Fed heads are talking out loud about unwinding QE and shedding some of the Treasuries on its balance sheet.
Inflation has picked up too, and Treasury yields have begun to rise, and when yields rise, bond prices fall, and so unloading US Treasuries at what might be seen as the peak may just be an investment decision by some official institutions.
The chart below from Goldman Sachs, via Christine Hughes at Otterwood Capital, shows the net transactions of US Treasury bonds and notes in billions of dollars by foreign official institutions (central banks, government funds, and the like) on a 12-month moving average. Note how it started with a whimper, bounced back a little, before turning into wholesale dumping, hitting record after record (red marks added):

The People’s Bank of China reported two days ago that foreign exchange reserves fell by another $12.3 billion in January, to $2.998 trillion, the seventh month in a row of declines, and the lowest in six years. They’re down 25%, or almost exactly $1 trillion, from their peak in June 2014 of nearly $4 trillion (via Trading Economics, red line added):

China’s foreign exchange reserves are composed of assets that are denominated in different currencies, but China does not provide details. So of the $1 trillion in reserves that it shed since 2014, not all were denominated in dollars.
The US Treasury Department provides another partial view, based on data collected primarily from US-based custodians and broker-dealers that are holding these securities for China and other countries. But the US Treasury cannot determine which country owns the Treasuries held in custodial accounts overseas. Based on this limited data, China’s holdings of US Treasuries have plunged by $215.2 billion, or 17%, over the most recent 12 reporting months through November, to just above $1 trillion.
So who is buying all these Treasuries when the formerly largest buyers – the Fed, China, and Japan – have stepped away, and when in fact China, Japan, and other countries have become net sellers, and when the Fed is thinking out loud about shedding some of the Treasuries on its balance sheet, just as nearly $900 billion in net new supply (to fund the US government) flooded the market over the past 12 months?
Turns out, there are plenty of buyers among US investors who may be worried about what might happen to some of the other hyper-inflated asset classes.
And for long suffering NIRP refugees in Europe, there’s a special math behind buying Treasuries. They’re yielding substantially more than, for example, French government bonds, with the US Treasury 10-year yield at 2.4%, and the French 10-year yield at 1.0%, as the ECB under its QE program is currently the relentless bid, buying no matter what, especially if no one else wants this paper. So on the face of it, buying US Treasuries would be a no-brainer.
But the math got a lot more one-sided in recent days as French government bonds now face a new risk, even if faint, of being re-denominated from euros into new French francs, against the will of bondholders, an act of brazen default, and these francs would subsequently get watered down, as per the euro-exit election platform of Marine Le Pen. However distant that possibility, the mere prospect of it, or the prospect of what might happen in Italy, is sending plenty of investors to feed on the richer yields sprouting in less chaos, for the moment at least, across the Atlantic.