
by National Mortgage Professional Magazine
Despite an improving job market and low interest rates, the share of first-time homebuyers fell to its lowest point in nearly three decades and is preventing a healthier housing market from reaching its full potential, according to an annual survey released by the National Association of Realtors (NAR). The survey additionally found that an overwhelming majority of buyers search for homes online and then purchase their home through a real estate agent.
The 2014 NAR Profile of Home Buyers and Sellers continues a long-running series of large national NAR surveys evaluating the demographics, preferences, motivations, plans and experiences of recent home buyers and sellers; the series dates back to 1981. Results are representative of owner-occupants and do not include investors or vacation homes.
The long-term average in this survey, dating back to 1981, shows that four out of 10 purchases are from first-time home buyers. In this year’s survey, the share of first-time home buyers dropped five percentage points from a year ago to 33 percent, representing the lowest share since 1987 (30 percent).
“Rising rents and repaying student loan debt makes saving for a down payment more difficult, especially for young adults who’ve experienced limited job prospects and flat wage growth since entering the workforce,” said Lawrence Yun, NAR chief economist. “Adding more bumps in the road, is that those finally in a position to buy have had to overcome low inventory levels in their price range, competition from investors, tight credit conditions and high mortgage insurance premiums.”
Yun added, “Stronger job growth should eventually support higher wages, but nearly half (47 percent) of first-time buyers in this year’s survey (43 percent in 2013) said the mortgage application and approval process was much more or somewhat more difficult than expected. Less stringent credit standards and mortgage insurance premiums commensurate with current buyer risk profiles are needed to boost first-time buyer participation, especially with interest rates likely rising in upcoming years.”
The household composition of buyers responding to the survey was mostly unchanged from a year ago. Sixty-five percent of buyers were married couples, 16 percent single women, nine percent single men and eight percent unmarried couples.
 In 2009, 60 percent of buyers were married, 21 percent were single women, 10 percent single men and 8 percent unmarried couples. Thirteen percent of survey respondents were multi-generational households, including adult children, parents and/or grandparents.
In 2009, 60 percent of buyers were married, 21 percent were single women, 10 percent single men and 8 percent unmarried couples. Thirteen percent of survey respondents were multi-generational households, including adult children, parents and/or grandparents.
The median age of first-time buyers was 31, unchanged from the last two years, and the median income was $68,300 ($67,400 in 2013). The typical first-time buyer purchased a 1,570 square-foot home costing $169,000, while the typical repeat buyer was 53 years old and earned $95,000. Repeat buyers purchased a median 2,030-square foot home costing $240,000.
When asked about the primary reason for purchasing, 53 percent of first-time buyers cited a desire to own a home of their own. For repeat buyers, 12 percent had a job-related move, 11 percent wanted a home in a better area, and another 10 percent said they wanted a larger home. Responses for other reasons were in the single digits.
According to the survey, 79 percent of recent buyers said their home is a good investment, and 40 percent believe it’s better than stocks.
Financing the purchase
Nearly nine out of 10 buyers (88 percent) financed their purchase. Younger buyers were more likely to finance (97 percent) compared to buyers aged 65 years and older (64 percent). The median down payment ranged from six percent for first-time buyers to 13 percent for repeat buyers. Among 23 percent of first-time buyers who said saving for a down payment was difficult, more than half (57 percent) said student loans delayed saving, up from 54 percent a year ago.
 In addition to tapping into their own savings (81 percent), first-time homebuyers used a variety of outside resources for their loan downpayment. Twenty-six percent received a gift from a friend or relative—most likely their parents—and six percent received a loan from a relative or friend. Ten percent of buyers sold stocks or bonds and tapped into a 401(k) fund.
In addition to tapping into their own savings (81 percent), first-time homebuyers used a variety of outside resources for their loan downpayment. Twenty-six percent received a gift from a friend or relative—most likely their parents—and six percent received a loan from a relative or friend. Ten percent of buyers sold stocks or bonds and tapped into a 401(k) fund.
Ninety-three percent of entry-level buyers chose a fixed-rate mortgage, with 35 percent financing their purchase with a low-down payment Federal Housing Administration-backed mortgage (39 percent in 2013), and nine percent using the Veterans Affairs loan program with no downpayment requirements.
“FHA premiums are too high in relation to default rates and have likely dissuaded some prospective first-time buyers from entering the market,” said Yun. “To put it in perspective, 56 percent of first-time buyers used a FHA loan in 2010. The current high mortgage insurance added to their monthly payment is likely causing some young adults to forgo taking out a loan.”
Buyers used a wide variety of resources in searching for a home, with the Internet (92 percent) and real estate agents (87 percent) leading the way. Other noteworthy results included mobile or tablet applications (50 percent), mobile or tablet search engines (48 percent), yard signs (48 percent) and open houses (44 percent).
According to NAR President Steve Brown, co-owner of Irongate, Inc., Realtors® in Dayton, Ohio, although more buyers used the Internet as the first step of their search than any other option (43 percent), the Internet hasn’t replaced the real estate agent’s role in a transaction.
“Ninety percent of home buyers who searched for homes online ended up purchasing their home through an agent,” Brown said. “In fact, buyers who used the Internet were more likely to purchase their home through an agent than those who didn’t (67 percent). Realtors are not only the source of online real estate data, they also use their unparalleled local market knowledge and resources to close the deal for buyers and sellers.”
When buyers were asked where they first learned about the home they purchased, 43 percent said the Internet (unchanged from last year, but up from 36 percent in 2009); 33 percent from a real estate agent; 9 percent a yard sign or open house; six percent from a friend, neighbor or relative; five percent from home builders; three percent directly from the seller; and one percent a print or newspaper ad.
Likely highlighting the low inventory levels seen earlier in 2014, buyers visited 10 homes and typically found the one they eventually purchased two weeks quicker than last year (10 weeks compared to 12 in 2013). Overall, 89 percent were satisfied with the buying process.
First-time home buyers plan to stay in their home for 10 years and repeat buyers plan to hold their property for 15 years; sellers in this year’s survey had been in their previous home for a median of 10 years.
 The biggest factors influencing neighborhood choice were quality of the neighborhood (69 percent), convenience to jobs (52 percent), overall affordability of homes (47 percent), and convenience to family and friends (43 percent). Other factors with relatively high responses included convenience to shopping (31 percent), quality of the school district (30 percent), neighborhood design (28 percent) and convenience to entertainment or leisure activities (25 percent).
The biggest factors influencing neighborhood choice were quality of the neighborhood (69 percent), convenience to jobs (52 percent), overall affordability of homes (47 percent), and convenience to family and friends (43 percent). Other factors with relatively high responses included convenience to shopping (31 percent), quality of the school district (30 percent), neighborhood design (28 percent) and convenience to entertainment or leisure activities (25 percent).
This year’s survey also highlighted the significant role transportation costs and “green” features have in the purchase decision process. Seventy percent of buyers said transportation costs were important, while 86 percent said heating and cooling costs were important. Over two-thirds said energy efficient appliances and lighting were important (68 and 66 percent, respectively).
Seventy-nine percent of respondents purchased a detached single-family home, eight percent a townhouse or row house, 8 percent a condo and six percent some other kind of housing. First-time home buyers were slightly more likely (10 percent) to purchase a townhouse or a condo than repeat buyers (seven percent). The typical home had three bedrooms and two bathrooms.
The majority of buyers surveyed purchased in a suburb or subdivision (50 percent). The remaining bought in a small town (20 percent), urban area (16 percent), rural area (11 percent) or resort/recreation area (three percent). Buyers’ median distance from their previous residence was 12 miles.
Characteristics of sellers
The typical seller over the past year was 54 years old (53 in 2013; 46 in 2009), was married (74 percent), had a household income of $96,700, and was in their home for 10 years before selling—a new high for tenure in home. Seventeen percent of sellers wanted to sell earlier but were stalled because their home had been worth less than their mortgage (13 percent in 2013).
“Faster price appreciation this past year finally allowed more previously stuck homeowners with little or no equity the ability to sell after waiting the last few years,” Yun said.
Sellers realized a median equity gain of $30,100 ($25,000 in 2013)—a 17 percent increase (13 percent last year) over the original purchase price. Sellers who owned a home for one year to five years typically reported higher gains than those who owned a home for six to 10 years, underlining the price swings since the recession.
The median time on the market for recently sold homes dropped to four weeks in this year’s report compared to five weeks last year, indicating tight inventory in many local markets. Sellers moved a median distance of 20 miles and approximately 71 percent moved to a larger or comparably sized home.
A combined 60 percent of responding sellers found a real estate agent through a referral by a friend, neighbor or relative, or used their agent from a previous transaction. Eighty-three percent are likely to use the agent again or recommend to others.
For the past three years, 88 percent of sellers have sold with the assistance of an agent and only nine percent of sales have been for-sale-by-owner, or FSBO sales.
For-sale-by-owner transactions accounted for 9 percent of sales, unchanged from a year ago and matching the record lows set in 2010 and 2012; the record high was 20 percent in 1987. The share of homes sold without professional representation has trended lower since reaching a cyclical peak of 18 percent in 1997.
Factoring out private sales between parties who knew each other in advance, the actual number of homes sold on the open market without professional assistance was 5 percent. The most difficult tasks reported by FSBOs are getting the right price, selling within the length of time planned, preparing or fixing up the home for sale, and understanding and completing paperwork.
NAR mailed a 127-question survey in July 2014 using a random sample weighted to be representative of sales on a geographic basis. A total of 6,572 responses were received from primary residence buyers. After accounting for undeliverable questionnaires, the survey had an adjusted response rate of 9.4 percent. The recent home buyers had to have purchased a home between July of 2013 and June of 2014. Because of rounding and omissions for space, percentage distributions for some findings may not add up to 100 percent. All information is characteristic of the 12-month period ending in June 2014 with the exception of income data, which are for 2013.

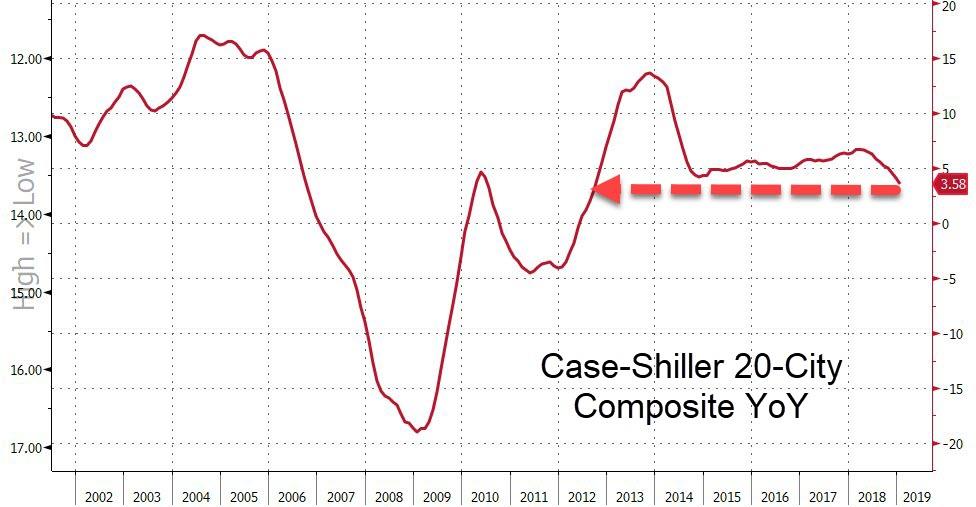


 GSE funding activity has dropped for the second consecutive year.
GSE funding activity has dropped for the second consecutive year. The 2018 year-to-date counts and volume balances were down 16 percent and 15 percent, respectively, compared to same nine months in 2016.
The 2018 year-to-date counts and volume balances were down 16 percent and 15 percent, respectively, compared to same nine months in 2016.









 In 2009, 60 percent of buyers were married, 21 percent were single women, 10 percent single men and 8 percent unmarried couples. Thirteen percent of survey respondents were multi-generational households, including adult children, parents and/or grandparents.
In 2009, 60 percent of buyers were married, 21 percent were single women, 10 percent single men and 8 percent unmarried couples. Thirteen percent of survey respondents were multi-generational households, including adult children, parents and/or grandparents. In addition to tapping into their own savings (81 percent), first-time homebuyers used a variety of outside resources for their loan downpayment. Twenty-six percent received a gift from a friend or relative—most likely their parents—and six percent received a loan from a relative or friend. Ten percent of buyers sold stocks or bonds and tapped into a 401(k) fund.
In addition to tapping into their own savings (81 percent), first-time homebuyers used a variety of outside resources for their loan downpayment. Twenty-six percent received a gift from a friend or relative—most likely their parents—and six percent received a loan from a relative or friend. Ten percent of buyers sold stocks or bonds and tapped into a 401(k) fund. The biggest factors influencing neighborhood choice were quality of the neighborhood (69 percent), convenience to jobs (52 percent), overall affordability of homes (47 percent), and convenience to family and friends (43 percent). Other factors with relatively high responses included convenience to shopping (31 percent), quality of the school district (30 percent), neighborhood design (28 percent) and convenience to entertainment or leisure activities (25 percent).
The biggest factors influencing neighborhood choice were quality of the neighborhood (69 percent), convenience to jobs (52 percent), overall affordability of homes (47 percent), and convenience to family and friends (43 percent). Other factors with relatively high responses included convenience to shopping (31 percent), quality of the school district (30 percent), neighborhood design (28 percent) and convenience to entertainment or leisure activities (25 percent).
You must be logged in to post a comment.